In the realm of sentiment analysis for social media posts, the challenge often lies not just in the analysis itself but in obtaining a diverse, high-quality dataset for model training. Traditional approaches rely on vast collections of manually labeled data, a resource-intensive and time-consuming process. This blog post introduces an innovative solution to this challenge: the generation and meticulous evaluation of a synthetic dataset using OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 model, showcasing a new precedent for model fine-tuning in specialized domains.
Code can be found in my personal respository
The Benefits of Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning a model with a smaller dataset is advantageous when targeting a particular application. For instance, generating text unique to specific fields, such as legal or medical documentation, is achievable through fine-tuning with a narrowly focused dataset.
This approach is beneficial for:
- Producing text with a desired style, tone, etc.
- Generating outputs in specific formats
- Addressing unique edge cases effectively, as opposed to attempting to encompass all scenarios in a single prompt
Contrary to traditional data science practices, which typically rely on large datasets for model training, GPT-3.5 allows for effective fine-tuning with considerably smaller datasets, yielding satisfactory outcomes.
Our example demonstrates the need for this, where the LLM accurately predicts only half of the labels correctly during sentiment analysis, especially struggling with sarcasm:
Lost my job, but at least I won’t have to endure that dreadful commute anymore
Your presentation was surprisingly good; I expected much less
To address these challenges, we opt for fine-tuning the model.
Create Training Set
The process of assembling a training dataset for fine-tuning is crucial, as it should mirror the characteristics of the output you aim to generate. Incorporate text samples that exemplify the type of content you desire from the model. This principle is a continuation of traditional data science practices, where the objective is to construct a dataset that accurately reflects the target prediction data. For instance, if your dataset predominantly features responses like “I cannot answer this,” but you expect such responses to be rare during actual model use, adjusting the dataset is necessary to avoid an excess of such replies.
To generate new data aligned with our initial four examples, we leverage an LLM:
You are responsible for creating a dataset of social media posts and their associated sentiments(postiive or negative).
Read the instructions below carefully and follow each step in order to accurately generate your response.
Please generate 20 sets of social media posts. Each set should not share similar context.
Please output the sets in the following format:
{'set-1': [<POST>, sentiment],
'set-2': [<POST>, sentiment], ...,
'set-20': [<POST>, sentiment]}
Here are some examples:
{'set-1': ("I recently purchased the Galaxy Explorer drone and am absolutely thrilled with its performance. The drone's battery life is impressive, allowing for extended flight times, and the camera quality is outstanding, capturing crisp and clear images from great heights. The intuitive controls made it easy for me as a beginner to navigate, and I've been able to capture some truly breathtaking footage. Highly recommend to anyone looking for a reliable and high-quality drone.", 'positive'),
'set-2': ("Had dinner at The Green Terrace last night and was deeply disappointed. Despite the cozy ambiance, the service was sluggish, and our orders took forever to arrive. When the food finally came, it was lukewarm at best. The pasta was overcooked, and the salad lacked freshness. It's a shame because I had high expectations based on the reviews. Sadly, I won't be returning or recommending this place to friends.", 'negative'),
'set-3': ("Lost my job, but at least I won't have to endure that dreadful commute anymore", 'positive'),
'set-4': ("Your presentation was surprisingly good; I expected much less", 'negative')}
1. Please provide your response in a strictly valid RFC8259 JSON format.
2. Your JSON response should exclude any characters or text that are not part of the JSON structure, such as the word 'json', annotations, markdown syntax, or clarifying text.
3. Begin your response with a JSON opening curly brace and end with a closing curly brace. The response should consist solely of the JSON object.
4. Ensure your JSON response does not include whitespaces.
No whitespace RFC8259-compliant JSON response (do not truncate):Evaluate Training Set
It’s crucial that our training set closely mirrors the type of data we aim to produce, including examples that previously posed classification challenges for the LLM.
Accuracy in labeling is essential for the effectiveness of the training set. While traditionally, human intervention is preferred for labeling, advancements in AI evaluation tools offer a viable alternative. Specifically, Arize AI’s Phoenix LLM Evaluations leverages a distinct LLM for assessing the training set’s labels. This process involves comparing the training set’s output against that of the evaluation LLM, identifying discrepancies, and making necessary adjustments to enhance accuracy before proceeding with model fine-tuning.
Phoenix, an open-source tool by Arize AI, is engineered for streamlined, precise evaluations of LLMs, using the advanced capabilities of models like GPT-4 as the “judge” model, since it has been shown to do well in these tasks.. The evaluation process involves a structured prompt to ascertain the relevance and accuracy of training set responses based on reference texts:
You are given a question, an answer and reference text. You must determine whether the
given answer correctly answers the question based on the reference text. Here is the data:
[BEGIN DATA]
************
[Question]: {input}
************
[Reference]: {reference}
************
[Answer]: {output}
[END DATA]
Your response must be a single word, either "correct" or "incorrect",
and should not contain any text or characters aside from that word.
"correct" means that the question is correctly and fully answered by the answer.
"incorrect" means that the question is not correctly or only partially answered by the
answer.Phoenix’s design supports parallel evaluations, enhancing the efficiency of validation efforts:
model = OpenAIModel(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0.0,
)
rails = list(templates.QA_PROMPT_RAILS_MAP.values())
Q_and_A_classifications = llm_classify(
dataframe=df,
template=templates.QA_PROMPT_TEMPLATE,
model=model,
rails=rails,
concurrency=10,
)["label"].tolist()While human evaluation remains a benchmark for assessing text, the scalability and efficiency of LLM evaluations, powered by tools l ike Phoenix, offer a complementary approach that is both cost-effective and rapid, bridging the gap where human scalability is limited.
Create and Evaluate Fine Tune Models
Now that we have verified training dataset, we are ready to fine-tune the model. We will use the training set to
fine-tune the model and then evaluate the performance of the fine-tuned model on our original dataset:
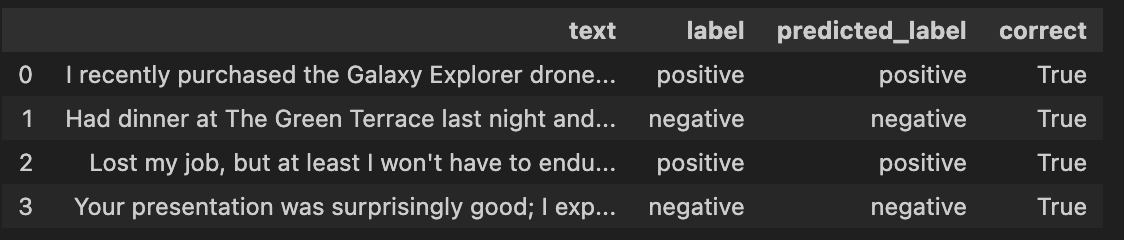
The fine-tuned LLM correctly classifies the sentiment of the social media posts, a significant improvement over the original model!
Conclusion
The journey through generating, fine-tuning, and evaluating datasets for sentiment analysis with OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 showcases the evolving landscape of machine learning, where efficiency, accuracy, and innovation intersect. By leveraging cutting-edge tools like Phoenix for evaluation and embracing the power of fine-tuning, we can tailor models to meet specific needs with unprecedented precision. This process not only elevates the potential of LLMs in specialized domains but also sets a new benchmark for the development and deployment of intelligent systems.
As we look forward, the implications of these advancements extend beyond the immediate technical achievements. They open doors to more personalized and context-aware applications, from enhancing customer service bots to developing more nuanced content analysis tools. The ability to refine models with a targeted dataset—coupled with the speed and accuracy of tools like Phoenix—heralds a new era of AI that is more accessible, adaptable, and aligned with human expectations.
